Quick Start¶
Get started with qpx in minutes - from installation to your first data conversion.
Quick Start Flow¶
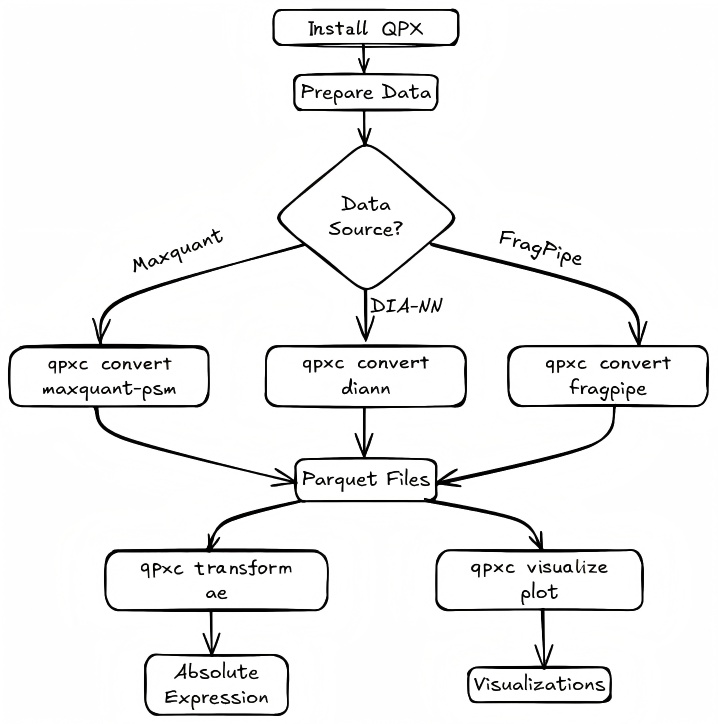
Prerequisites¶
Before installing qpx, ensure you have:
- Python 3.10 or higher - Check with
python --version - pip - Python package manager (included with Python)
- Optional: conda/mamba for environment management
Installation¶
Verify Installation¶
After installation, verify qpx is working correctly:
You should see output similar to:
Usage: qpxc [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
qpx command line interface for proteomics data processing.
Options:
--version Show the version and exit.
--help Show this message and exit.
Commands:
convert Convert proteomics data formats to QPX format
project Project management commands
stats Statistical analysis commands
transform Data transformation commands
visualize Visualization commands
Your First Conversion¶
Let's convert some sample MaxQuant data to QPX format.
Step 1: Download Sample Data¶
# Create a working directory
mkdir qpx-tutorial && cd qpx-tutorial
# Download sample MaxQuant msms.txt file
curl -L -o msms.txt \
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/bigbio/qpx/main/tests/examples/maxquant/maxquant_simple/msms.txt"
Step 2: Convert to QPX Format¶
# Convert MaxQuant PSM data to QPX parquet format
qpxc convert maxquant-psm \
--msms-file msms.txt \
--output-folder ./output \
--verbose
Step 3: Verify the Output¶
Step 4: Inspect the Data (Optional)¶
# Using Python to read the parquet file
import pyarrow.parquet as pq
table = pq.read_table("output/psm-*.psm.parquet")
df = table.to_pandas()
print(f"Total PSMs: {len(df)}")
print(f"Columns: {list(df.columns)}")
print(df.head())
What's Next?¶
Now that you've completed your first conversion, explore more:
| Next Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Examples Overview | More conversion and analysis examples |
| Convert Commands | All available data converters |
| Transform Commands | Data transformation tools |
| Format Specification | Understanding QPX data formats |
Common Commands¶
# Convert DIA-NN data
qpxc convert diann --report-path report.tsv --output-folder ./output
# Convert FragPipe data
qpxc convert fragpipe --psm-file psm.tsv --output-folder ./output
# Generate statistics
qpxc stats analyze psm --parquet-path ./output/psm.parquet
# Create visualizations
qpxc visualize plot ibaq-distribution --ibaq-path ./output/ae.parquet
Need Help?¶
- Run
qpxc <command> --helpfor detailed command help - Check the Troubleshooting guide
- Visit our GitHub Issues for support